Case Report - (2022) Volume 7, Issue 9
Electroacupuncture Combined with A Classic Herbal Formula in The Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: A Case Report
2Acupuncture Wellness Center of Cincinnati, 5887 Unit#4 Cornell Rd., Cincinnati, OH, USA
Received Date: Aug 11, 2022 / Accepted Date: Aug 22, 2022 / Published Date: Sep 05, 2022
Abstract
This article presents the case report of a 47-year-old man who was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes and a high hemoglobin A1C level, 26%. He wanted to be treated by Traditional Chinese Medicine (acupuncture and Chinese herbs) to improve his health and decrease his level of blood sugar. The goal of the treatment is to reduce the level of hemoglobin A1C to 7%, as requested by his family doctor.
Outcomes: For 4 months, electroacupuncture was done once a week in combination with the classic herbal formula of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang which was taken three times a day in the form of tea, the result of which was the patient’s level of hemoglobin A1C dropped from 26% to 7%.
Conclusion: This case shows that electroacupuncture combined with the classic herbal formula HLJDT not only effectively reduces blood sugar and the hemoglobin A1C level, but it also significantly improves the subjective symptoms, helps patients to reduce the doses of medication, and prevents the progression of Type 2 diabetes.
Keywords
Type 2 diabetes, TCM, Electroacupuncture, Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang (HLJDT)
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease in which the body does not produce enough or respond normally to insulin, causing blood sugar (glucose) levels to be abnormally high [1]. The main clinical manifestations of DM are polydipsia, polyphagia, and polyuria [2]. Type 2 diabetes is one of the types of Diabetes mellitus that usually affects older adults [1]. More than 95% of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes [3]. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease that negatively affects the body’s ability to properly use energy from food. It is also called type 2 diabetes mellitus and adult-onset diabetes [4]. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the cells of the body resist the normal effect of insulin, which is to drive glucose from the blood into the cells of the body. This condition is called insulin resistance. As a result, glucose starts to build up in the blood. 4 The symptoms of type 2 diabetes include the following: unusual thirst, frequent urination, weight change (gain or loss), extreme fatigue or lack of energy, blurred vision, frequent or recurring infections, cuts and bruises that are slow to heal, tingling or numbness in the hands or feet, trouble getting or maintaining an erection, diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) [5]. Ninety percent of Canadians with diabetes have type 2 diabetes [5]. Type 2 diabetes negatively affects the nation’s health and economy.
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is called “emaciation-thirst disease” (in Chinese Xiaokebing æ¶?渴ç??). In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) it is associated with the clinical manifestations of weight loss, polyphagia, polydipsia, polyuria and sweet urine. According to TCM, DM is divided into Upper Jiao diabetes due to excess heat in the lungs; Middle Jiao diabetes due to excess heat in the stomach, and Lower Jiao diabetes due to the deficiency of kidney yin. The TCM treatise The Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Internal Medicine (in Chinese Huangdi Neijing é»?å¸å??ç») believes that eating too many fatty, sweet and rich foods causes heat to arise from the stomach. As a consequence of the accumulation of the heat, body fluids are consumed, and diabetes mellitus develops. The understanding of and the therapy recommended for diabetes mellitus in TCM has a history of 2,000 years in China. Many physicians in past dynasties analyzed the pathogenesis and treatment of this disease from multiple perspectives. Zhang Xichun (1860–1933), the medical master of Chinese medicine in modern times, pioneered the research on the treatment of diabetes mellitus in TCM. He proposed that diabetes was caused by a lack of vital qi, the decline of the pectoral qi, and the inability of the spleen to disperse the essence of the spleen [6]. In addition, some physicians believe that he pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus is due to yin deficiency and dryness and heat. Accordingly, the therapeutic principles of treatment are aimed at “clearing heat and moistening dryness, nourishing yin and producing body fluid” [7].
Clinical Case
Patient Information
A 47-year-old man, Canadian. His first consultation was on March 10, 2022 at Acuenergie Clinic. He had been diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. His main complaint was high levels of blood sugar (his Hemoglobin A1C level was 26% in February 2022). The dose of medication Pro-Metformin he took orally was 500 mg tablets twice a day. His doctor wanted to increase the dose to 1000 mg if the Hemoglobin A1C level could not be reduced to 7%. His symptoms were increased thirst, urination and hunger; hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), exhaustion, irritability and impatience, yellow urine, excessive urination during the night, thirst with a dry mouth and throat, weight loss, dull pain in the liver and spleen areas, lower back pain on and off. He had a bowel movement with dry stools once a day in the morning after breakfast at 7am. He had abdominal distension after eating. His tongue was red with a yellow coating, cracks in the middle with tooth marks on the side, and the tip of his tongue had begun to atrophy. His pulse was rapid and strong. His abdominal ultrasound showed a fatty liver.
TCM Diagnosis: a deficiency of kidney and spleen qi, stagnation of liver qi, and heat accumulation in the Triple Burner.
Acupuncture Treatment Strategy: Invigorate the kidney and spleen qi, soothe liver qi, and eliminate body heat.
Method
Treatment protocol: acupuncture once a week and a classic herbal formula of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang twice a day.
Acupuncture protocol and acupoints
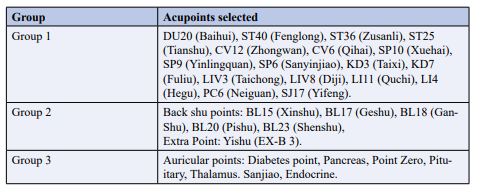
Table 1: Group of Acupoints
Frequency: 1 treatment a week, 12 times per treatment course. 3 groups of acupoints were used alternately.
Acupuncture Manipulation
After disinfecting all points with a cotton ball dipped in alcohol, the order of inserting the needles is from the lower limbs to the abdomen, starting on the left side and finishing on the right side. Disposable sterile needles, size 0.25x25mm, are used and are inserted perpendicularly in all points to a depth of 10 to 15mm with the Tonification-Purgation technique. An electro-acupuncture stimulator (model KWD-808I, brand Greatwall) is connected ipsilateral at four anterior acupoints, LI11 (Quchi) and PC6 (Neiguan), ST36 (Zusanli) and SP6 (Sanyinjiao), and at four posterior acupoints, BL15 (Xinshu) and Yishu (EX-B 3), BL20 (Pishu) and BL23 (Shenshu), and set to a continuous wave, the intensity of which is based on the patient's preference. Needles remain inserted for 30 minutes each session and acupuncture points are needled bilaterally and alternately.
Classic herbal formula HUANG-LIAN-JIE-DU-TANG (HLJDT)
Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang (HLJDT in Chineseé»?è¿?解æ¯?汤) is the classic herbal formula in traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) used for heat clearance and detoxification. It is taken from the Handbook of Prescriptions for Emergency (in Chinese Zhouhou Beiji Fang è??Ã¥ÂÂ?å¤?æ?¥æ?¹) written in the Eastern Jin Dynasty [8]. HLJDT has been widely used to treat inflammation, toxic heat syndromes, and infectious diseases since the Tang dynasty [9]. Recently, the benefits of HLJDT on diabetes were noted when it was used to treat diabetic patients [10]. The research suggests that the longterm administration of HLJDT could have protective effects on the vascular endothelium in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) due to its antioxidant properties and its attenuation of inflammatory mediators. The findings indicate that HLJDT could have a positive effect on diabetic vascular disease and could be used to prevent and treat the vascular complications of T2DM [11].
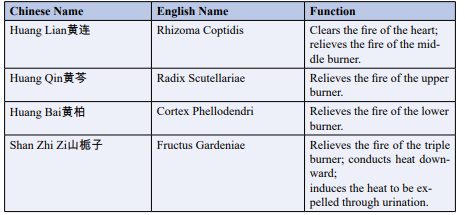
Table 2: The constituents of the herbal formula HLJDT
HLJDT Dosage and Administration
The patient takes the concentrated extract powder of the herbal formula HLJDT three times a day in the form of tea, 3 grams each time (the ratio of extract powder to raw herbs is 1:5). The herbal formula was processed into concentrated powders by KODA Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. in Taiwan.
Outcomes
After 4 months of TCM treatments of electroacupuncture combined with the classic herbal formula HLJDT, the Hemoglobin A1C levels dropped to 7% (the level requested by his doctor, see table 3). And blood glucose levels dropped and stayed between 5.2 and 6.4 mmol/L fasting (See tables 4). The pain in the liver and spleen areas disappeared. Excessive sweating decreased. Sleep improved, and his energy recovered, that is he no longer felt tired during the day. His bowel movement was regulated to between 6 am and 7am before breakfast. Urination during the night was reduced to once a night.

Table 3: Hemoglobin A1C level (%) The A1C test is a common blood test used to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The A1C test is also called the glycated hemoglobin, glycosylated hemoglobin, hemoglobin A1C or HbA1c test [12].
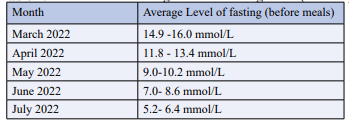
Table 4: Self-monitored average level of blood glucose (mmol/L)
Discussion
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces.1 Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has formed a complete knowledge system for diabetes mellitus and has a profound and unique understanding of its etiology and pathogenesis, course and prognosis, the susceptible population, complications, treatment principles, and nursing methods. The etiology of diabetes mellitus includes deficiency of viscera; improper diet; emotional disorders; injured kidneys. The pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus is due to a metabolic disorder of the viscera that manifests specifically in the following aspects: stomach heat, weak spleen, heart fire, lung dryness, liver stagnation, phlegm and dampness, and kidney deficiency.
Type 2 diabetes belongs to the category of Xiaokebing (in Chinese æ¶?渴ç??) in TCM. The etiology and pathogenesis of Type 2 diabetes in TCM are kidney and spleen yang deficiency, liver qi stagnation, excessive heat, yin deficiency, fire hyperactivity and qi-yin deficiency. The strategy of acupuncture treatment in this case is to invigorate the kidney and spleen qi, soothe the liver and regulate qi, and eliminate body heat using three groups of acupoints (see the section 2.2 Methods). Acupuncture treatment for this disease is not only used to control blood sugar levels, it can also help the other symptoms of frequent urination, thirst, fatigue and digestion issues. Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang (HLJDT) is the classic herbal formula of traditional Chinese medicine for heat clearance and detoxification, which is used in diabetic patients in the clinical practice of traditional Chinese medicine. For Type 2 diabetic patients, achieving a hemoglobin A1C level of 7% or less and self-monitoring blood glucose levels below 8.6 mmol/L are common goals of treatment [12]. The treatment methods of electroacupuncture combined with the classic herbal formula HLJDT helped the Type 2 diabetic patient reach this goal.
A change in lifestyle is very important after the blood sugar level has been controlled by TCM. A healthy diet (Low-Glycemic Index Food), regular exercise, and weight control are helpful in maintaining the A1C level in a normal range for Type 2 diabetic patients. It is important to adjust one’s lifestyle by eliminating raw food, cold beverages, sugar and saturated fats, coffee and alcohol; by eating 3 meals a day, going to sleep early and quitting smoking. In addition, not ruminating is essential as peace of mind and a stable mood are very important in the clinical treatment of Type 2 diabetes.
Patient’s Perspective
The patient was satisfied with the results. He willingly followed the treatment protocol and after the course of treatment finished, he continued with the herbal formula on his own.
Conclusion
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an effective complementary and alternative medicine in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. It is a good combination of routine antidiabetic drugs to improve diabetic syndromes without side-effects. This case shows that electroacupuncture combined with the classic herbal formula HLJDT not only effectively reduces blood sugar and the hemoglobin A1C level, but it also significantly improves the subjective symptoms, helps patients to reduce the doses of medication, and prevents the progression of Type 2 diabetes. This case also shows that TCM is an effective method of improving a patient’s health outcomes naturally.
Authorship and Contributions
Xiangping Peng wrote the manuscript. Guanhu Yang contributed on the use of Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) theory for Type 2 Diabetes.
Acknowledgement
Acknowledgements I would like to acknowledge and thank Andrea Saunderson for reviewing the English in this article.
References
1. Merck manual (2020) Diabetes Mellitus (DM) by Erika F. Brutsaert, New York Medical College, Last full review/revision Sep 2020.
2. PDB-101 (2017) The main symptoms of diabetes. April 2017, Jennifer Jiang, Dr. Shuchismita Dutta.
3. The World Health Organization (WHO) (2022) Diabetes.
4. Harvard Health Publishing -Type 2 diabetes mellitus February 23, 2022.
5. Type 2 symptoms. (2022). Diabetes Canada (2022). 6. Zhang X. (2010). Medical Essays Esteeming the East and Respecting the West. Taiyuan: Shanxi Science and Technology Press.
7. Tong X. (2016). Guidelines for clinical evidence-based practice of traditional Chinese medicine in diabetes. Beijing: Science Press.
8. Ge H. (2018), Handbook of Prescriptions for Emergency. Bejing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Publishing House.
9. Lu, J., Wang, J. S., & Kong, L. Y. (2011). Anti-inflammatory effects of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction, its two fractions and four typical compounds. Journal of ethnopharmacology, 134(3), 911-918.
10. Tian, W. H., Lu, B., & Hu, X. J. (2008). Huanglian Jiedu decoction treated the diabetes 32 cases. Shaanxi J Trad Chin Med, 29, 1603-1605.
11. Yi, Q., He, X. E., Luo, K. F., Zhang, G. S., Liu, Y. H., Xue, Q., ... & Luo, J. D. (2012). Protection of long-term treatment with huang-lian-jie-du-tang on vascular endothelium in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Current Therapeutic Research, 73(6), 174-185.
12. Mayo clinic, A1C test. (2022).
Copyright: © 2025 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.



